One way to bring together information from multiple source systems is to use a data platform. This allows you to freely access all data. This goes further than, for example, a CRM system with customer information and sales data that can only be used for CRM functionalities. It's all about opening up the source data to other applications, for analysis and data science applications. A data platform provides a layered structure for storing, classifying, filtering and cleaning data. The right, high-quality data - the goal of data-oriented work - is the basis for the analyses that you can do with it and determines the extent to which you can start working in a data-driven way.
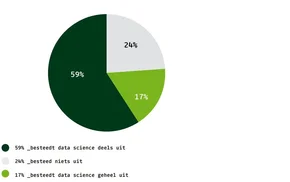
82% of the organizations indicate that they do not yet have their own data platform for data science applications. The 18% who do use it cite, among others, their own software, Azure, Power BI, Cognos, Google or Oracle.
Data governance
A data platform is a place where many different, sometimes sensitive, pieces of data come together. It is also the place where you determine who has access to which data: authorization. Or how long data may be retained: data retention. This ensures that the organization continues to comply with privacy legislation. For government organizations, there are also other guidelines, such as purpose limitation: the collection of data only for a specific purpose. When setting up a data platform, authorization and additional guidelines for responsible data use are laid down in a governance structure for the data platform as a whole.